6.3: Cancer and the Cell Cycle. Cancer is a collective name for many different diseases caused by a common mechanism: uncontrolled cell division. Despite the redundancy and overlapping levels of cell-cycle control, errors occur. One of the critical processes monitored by the cell-cycle checkpoint surveillance mechanism is the proper replication
Genes | Free Full-Text | Advancement in Human Face Prediction Using DNA
The size of an organ or organism depends mainly on its total cell mass, which depends on both the total number of cells and the size of the cells. Cell number, in turn, depends on the amounts of cell division and cell death. Organ and body size are therefore determined by three fundamental processes: cell growth, cell division, and cell death
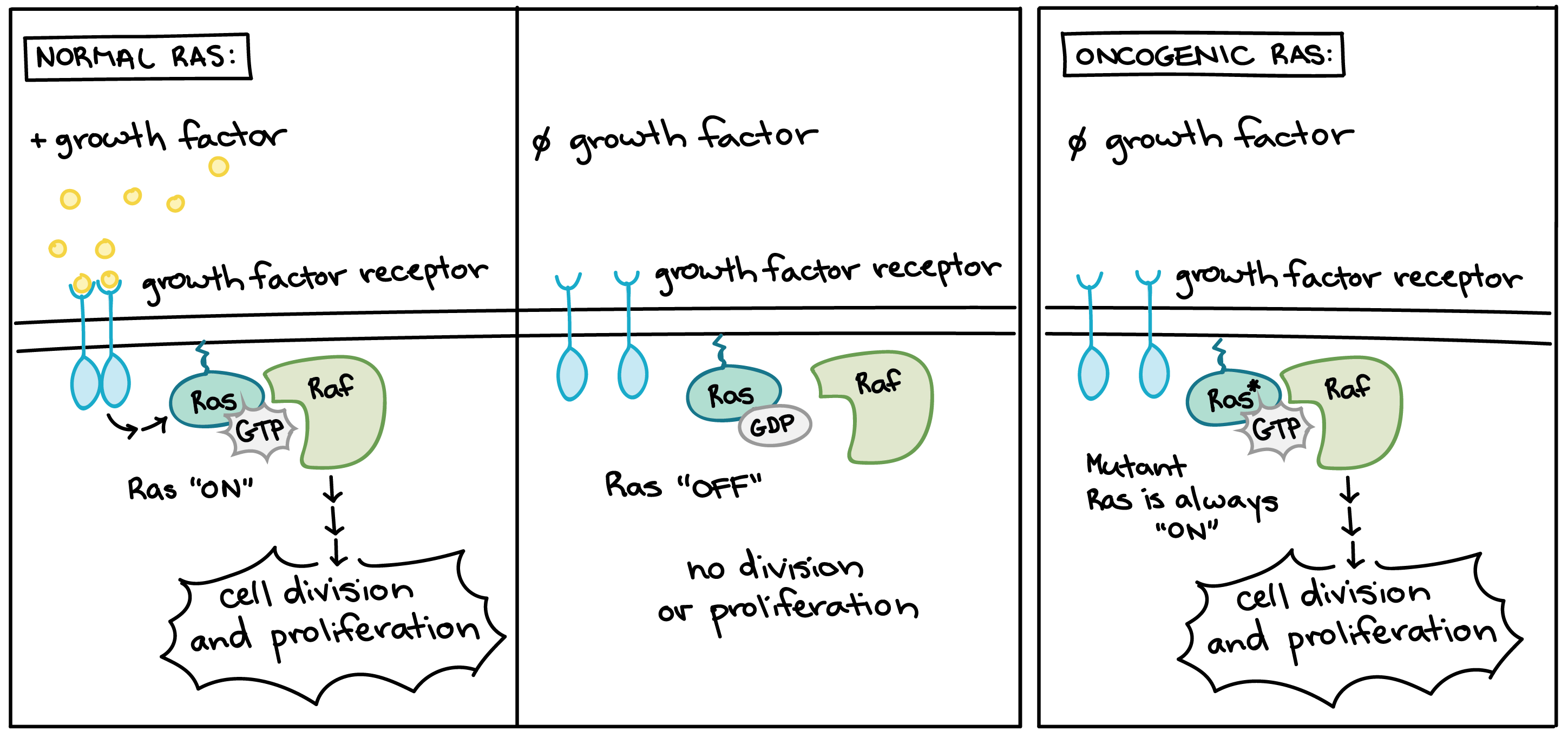
Source Image: bio1220.biosci.gatech.edu
Download Image
Cell cycle regulation, cancer, and stem cells. Cells in your body are dividing all the time. If they’re healthy cells, they divide in a carefully controlled way, proceeding with division only when conditions are right. Cancer cells, on the other hand, divide in an uncontrolled way. Learn more about cell cycle control, cancer cells, and stem cells.

Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Mutation, radiation – Biology Notes for IGCSE 2014
Cancer is a collective name for many different diseases caused by a common mechanism: uncontrolled cell division. Despite the redundancy and overlapping levels of cell-cycle control, errors occur. One of the critical processes monitored by the cell-cycle checkpoint surveillance mechanism is the proper replication of DNA during the S phase.
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
What Causes Uncontrolled Cell Division At The Genetic Level
Cancer is a collective name for many different diseases caused by a common mechanism: uncontrolled cell division. Despite the redundancy and overlapping levels of cell-cycle control, errors occur. One of the critical processes monitored by the cell-cycle checkpoint surveillance mechanism is the proper replication of DNA during the S phase.
Cell division is a fundamental process for life, but its molecular mechanisms are still not fully understood. This article reviews the recent advances in using various tools and approaches, such as genetics, biochemistry, microscopy, and computational modeling, to dissect the mechanisms of cell division in different organisms and systems. The article also discusses the challenges and
Since fertilization produces all cells in the body, where do germ cells in the offspring originate from, if they are not a product of somatic cell division? – Quora
The car keeps racing at top speed. In the case of a cell, the cell keeps dividing out of control, which can lead to cancer. Tumor suppressor genes are genes that normally slow down or stop cell division. When a mutation occurs in a tumor suppressor gene, it can no longer control cell division. This is like a car without brakes.
Biology Notes for A level: #32 Summary of Cell and Nuclear division

Source Image: biology4alevel.blogspot.com
Download Image
Biology Notes for A level: #32 Summary of Cell and Nuclear division
The car keeps racing at top speed. In the case of a cell, the cell keeps dividing out of control, which can lead to cancer. Tumor suppressor genes are genes that normally slow down or stop cell division. When a mutation occurs in a tumor suppressor gene, it can no longer control cell division. This is like a car without brakes.

Source Image: biology4alevel.blogspot.com
Download Image
Genes | Free Full-Text | Advancement in Human Face Prediction Using DNA
Cell cycle regulation, cancer, and stem cells. Cells in your body are dividing all the time. If they’re healthy cells, they divide in a carefully controlled way, proceeding with division only when conditions are right. Cancer cells, on the other hand, divide in an uncontrolled way. Learn more about cell cycle control, cancer cells, and stem cells.
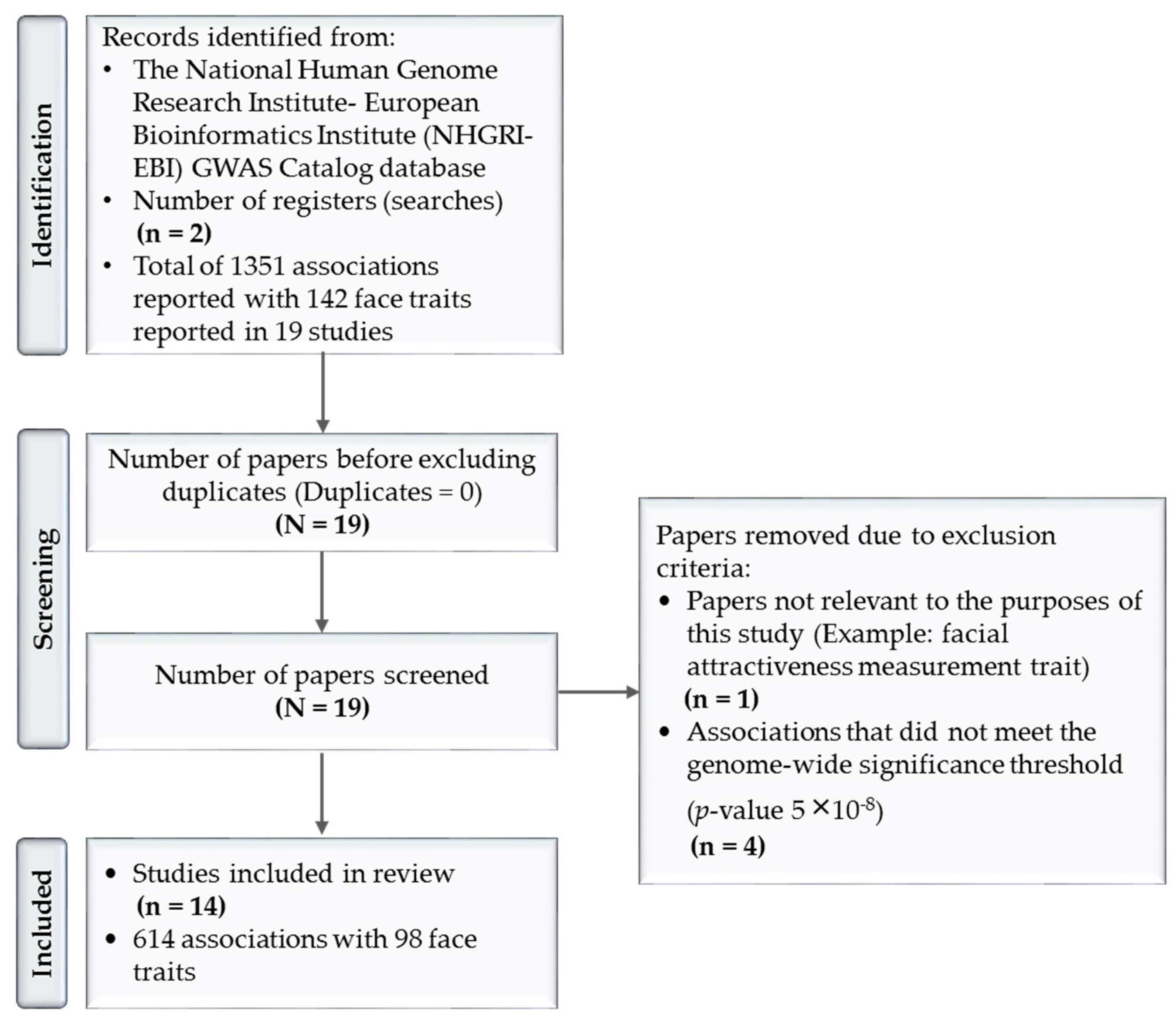
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
Mutation, radiation – Biology Notes for IGCSE 2014
6.3: Cancer and the Cell Cycle. Cancer is a collective name for many different diseases caused by a common mechanism: uncontrolled cell division. Despite the redundancy and overlapping levels of cell-cycle control, errors occur. One of the critical processes monitored by the cell-cycle checkpoint surveillance mechanism is the proper replication
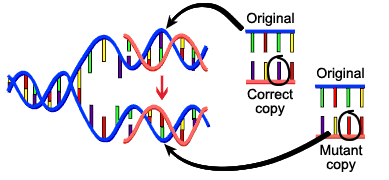
Source Image: biology-igcse.weebly.com
Download Image
Cancer. – ppt download
Connection for AP ® Courses. Cancer results from unchecked cell division caused by a breakdown of the mechanisms that regulate the cell cycle. The loss of control begins with a change in the DNA sequence of a gene that codes for one of the regulatory molecules. Faulty instructions lead to a protein that does not function as it should.
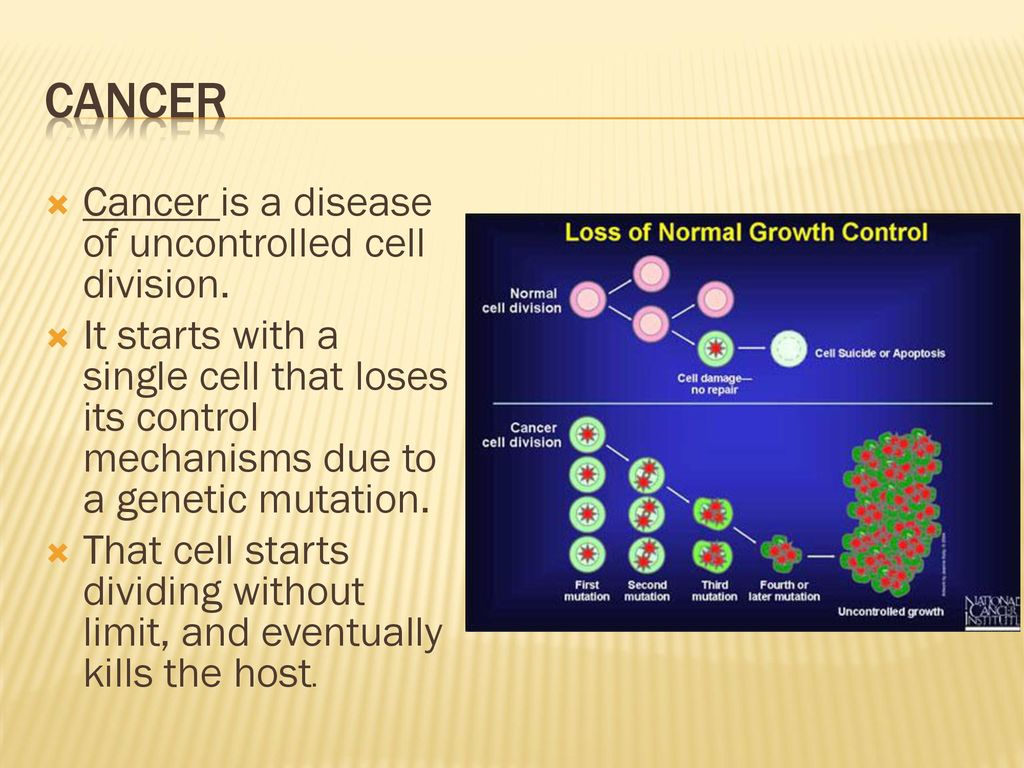
Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
1) Division and differentiation in human cells – ppt download
Cancer is a collective name for many different diseases caused by a common mechanism: uncontrolled cell division. Despite the redundancy and overlapping levels of cell-cycle control, errors occur. One of the critical processes monitored by the cell-cycle checkpoint surveillance mechanism is the proper replication of DNA during the S phase.

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
Why is synthesis important in the cell cycle? – Quora
Cell division is a fundamental process for life, but its molecular mechanisms are still not fully understood. This article reviews the recent advances in using various tools and approaches, such as genetics, biochemistry, microscopy, and computational modeling, to dissect the mechanisms of cell division in different organisms and systems. The article also discusses the challenges and
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Biology Notes for A level: #32 Summary of Cell and Nuclear division
Why is synthesis important in the cell cycle? – Quora
The size of an organ or organism depends mainly on its total cell mass, which depends on both the total number of cells and the size of the cells. Cell number, in turn, depends on the amounts of cell division and cell death. Organ and body size are therefore determined by three fundamental processes: cell growth, cell division, and cell death
Mutation, radiation – Biology Notes for IGCSE 2014 1) Division and differentiation in human cells – ppt download
Connection for AP ® Courses. Cancer results from unchecked cell division caused by a breakdown of the mechanisms that regulate the cell cycle. The loss of control begins with a change in the DNA sequence of a gene that codes for one of the regulatory molecules. Faulty instructions lead to a protein that does not function as it should.