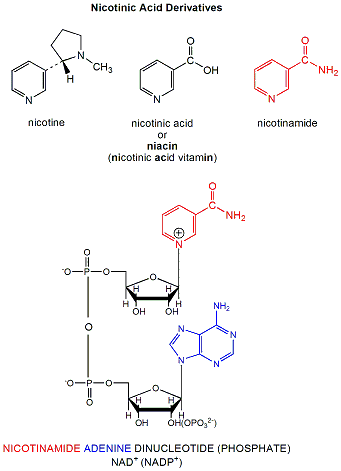
NAD+ and NADP+ are derivatives of nicotinic acid or nicotinamide. They intervene in biological redox reactions. Figure: NAD is a derivative of nicotinic acid or nicotinamide. NADP+ contains an additional phosphate group. Both NAD+ and NADP+ can undergo two electron redox steps, in which a hydride is transferred from an organic molecule to the
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
May 14, 2022NAD participates in many redox reactions in cells, including those in glycolysis and most of those in the citric acid cycle of cellular respiration. NADP is the reducing agent produced by the light reactions of photosynthesis and is consumed in the Calvin cycle of photosynthesis and used in many other anabolic reactions in both plants and animals.
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
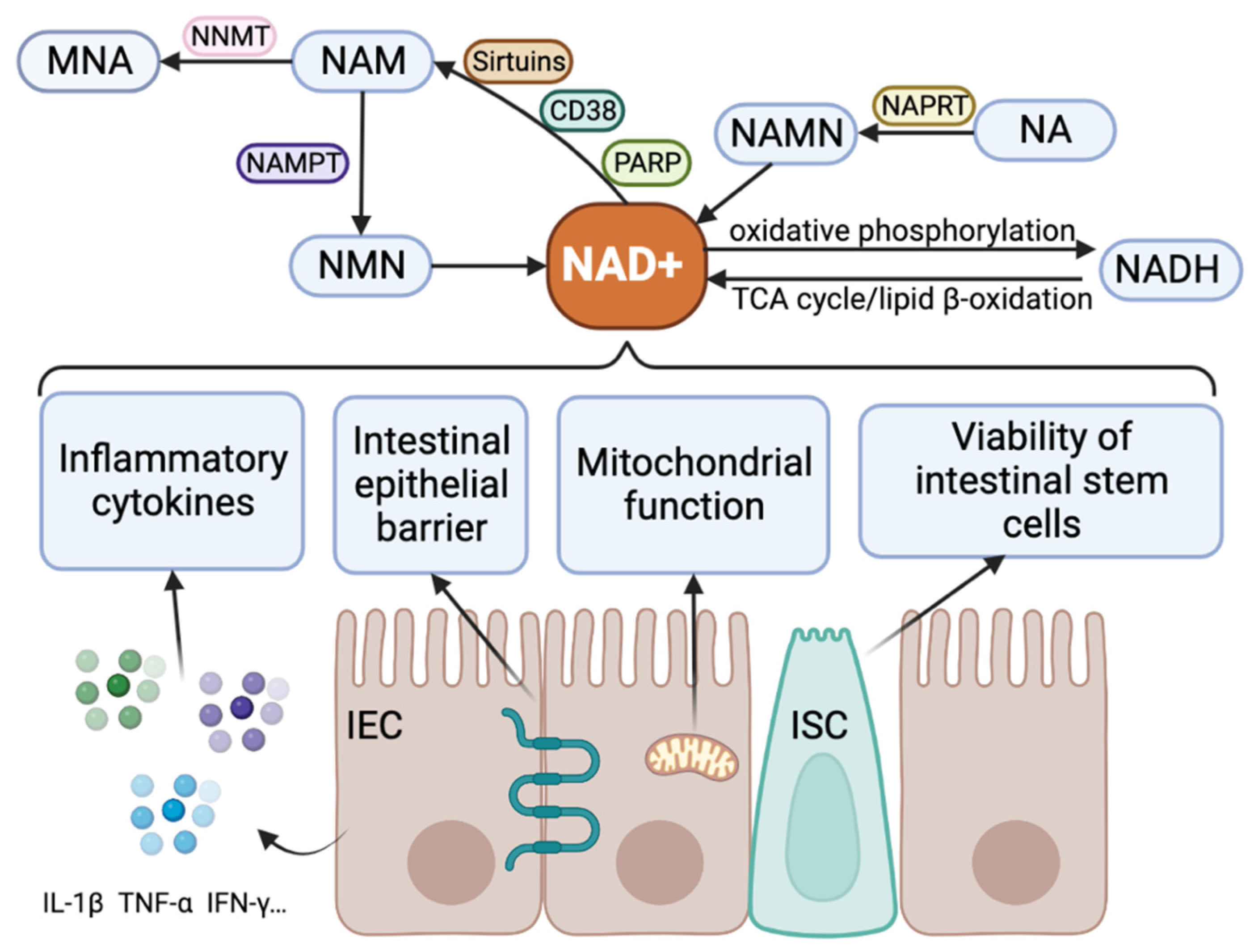
Feb 3, 2023NAD+ is an important factor in aging and the development of age-related diseases in the role of a cofactor in redox reactions and a coenzyme in metabolic processes. It also has a decisive role in non-redox reactions, such as cellular signal transduction, when acting as a substrate for sirtuins and PARPs . Sirtuins, PARPs and CD38 all compete

Source Image: serenity.ae
Download Image
Biomolecules | Free Full-Text | NADH/NAD+ Redox Imbalance and Diabetic Kidney Disease
In this video, we’re going to look at the biological redox reactions of alcohols in phenols. Over here on the left, we have the ethanol molecule. So this is our 2-carbon alcohol. And the carbon that we’re most concerned with is this carbon right here, which has one bond to this oxygen atom. And in the liver, ethanol is oxidized to ethanal.

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
What Role Does Nad+ Play In Redox Reactions
In this video, we’re going to look at the biological redox reactions of alcohols in phenols. Over here on the left, we have the ethanol molecule. So this is our 2-carbon alcohol. And the carbon that we’re most concerned with is this carbon right here, which has one bond to this oxygen atom. And in the liver, ethanol is oxidized to ethanal.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD +) is a coenzyme for redox reactions, making it central to energy metabolism. NAD + is also an essential cofactor for non-redox NAD + -dependent enzymes, including sirtuins, CD38 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases. NAD + can directly and indirectly influence many key cellular functions, including metabolic
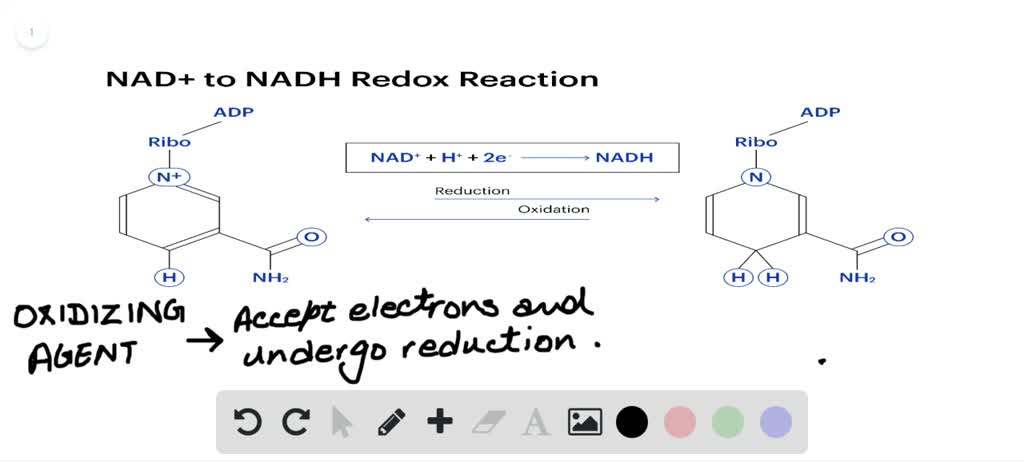
SOLVED: Identify the correct statement regarding NAD+ NAD+ can take part in only 2 electron oxidations NAD+ can take part in either one or two electron oxidations. NAD+ accepts two hydrogen atoms
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is a central redox factor and enzymatic cofactor that functions in a plethora of cellular processes, including metabolic pathways and DNA metabolism, and
Solved Question 11 The image below shows the redox reaction | Chegg.com

Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
7.8: The Chemistry of NAD+ and FAD – Chemistry LibreTexts
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is a central redox factor and enzymatic cofactor that functions in a plethora of cellular processes, including metabolic pathways and DNA metabolism, and
Source Image: chem.libretexts.org
Download Image
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
NAD+ and NADP+ are derivatives of nicotinic acid or nicotinamide. They intervene in biological redox reactions. Figure: NAD is a derivative of nicotinic acid or nicotinamide. NADP+ contains an additional phosphate group. Both NAD+ and NADP+ can undergo two electron redox steps, in which a hydride is transferred from an organic molecule to the

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Biomolecules | Free Full-Text | NADH/NAD+ Redox Imbalance and Diabetic Kidney Disease
Feb 3, 2023NAD+ is an important factor in aging and the development of age-related diseases in the role of a cofactor in redox reactions and a coenzyme in metabolic processes. It also has a decisive role in non-redox reactions, such as cellular signal transduction, when acting as a substrate for sirtuins and PARPs . Sirtuins, PARPs and CD38 all compete

Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
Electron Carriers in Cellular Respiration | Role & Process – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com
The nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+/NADH) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+/NADPH) redox couples function as cofactors or/and substrates for numerous enzymes to retain

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Redox reaction – Definition and Examples – Biology Online Dictionary
In this video, we’re going to look at the biological redox reactions of alcohols in phenols. Over here on the left, we have the ethanol molecule. So this is our 2-carbon alcohol. And the carbon that we’re most concerned with is this carbon right here, which has one bond to this oxygen atom. And in the liver, ethanol is oxidized to ethanal.
Source Image: biologyonline.com
Download Image
⏩SOLVED:What role does NAD^+ play in redox reactions? a. NAD^+ , an… | Numerade
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD +) is a coenzyme for redox reactions, making it central to energy metabolism. NAD + is also an essential cofactor for non-redox NAD + -dependent enzymes, including sirtuins, CD38 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases. NAD + can directly and indirectly influence many key cellular functions, including metabolic
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
7.8: The Chemistry of NAD+ and FAD – Chemistry LibreTexts
⏩SOLVED:What role does NAD^+ play in redox reactions? a. NAD^+ , an… | Numerade
May 14, 2022NAD participates in many redox reactions in cells, including those in glycolysis and most of those in the citric acid cycle of cellular respiration. NADP is the reducing agent produced by the light reactions of photosynthesis and is consumed in the Calvin cycle of photosynthesis and used in many other anabolic reactions in both plants and animals.
Biomolecules | Free Full-Text | NADH/NAD+ Redox Imbalance and Diabetic Kidney Disease Redox reaction – Definition and Examples – Biology Online Dictionary
The nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+/NADH) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+/NADPH) redox couples function as cofactors or/and substrates for numerous enzymes to retain